
Photo by André François McKenzie on Unsplash
Trust in Motion: Decentralized ETFs and the Onchain Advantage
Introduction
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a kind of investment fund that trades on stock exchanges similarly to individual stocks and tracks the price of an underlying asset, in this instance, Bitcoin.
They are designed to track the performance of bitcoin and keeping it as an underlying asset, derive the value for shares that represent ownership of the fund. These shares are accessible through regular brokerage accounts.
We will be understanding the existing mechanisms by which Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) currently operate.
Then explore the means to hybrid onchain ETFs for a more secure and decentralized approach to such investments which will introduce a more transparent means for investors to participate in these ETFs. Such a system will also empower the core values of Defi as compared to current models.
Understanding Traditional ETF Frameworks
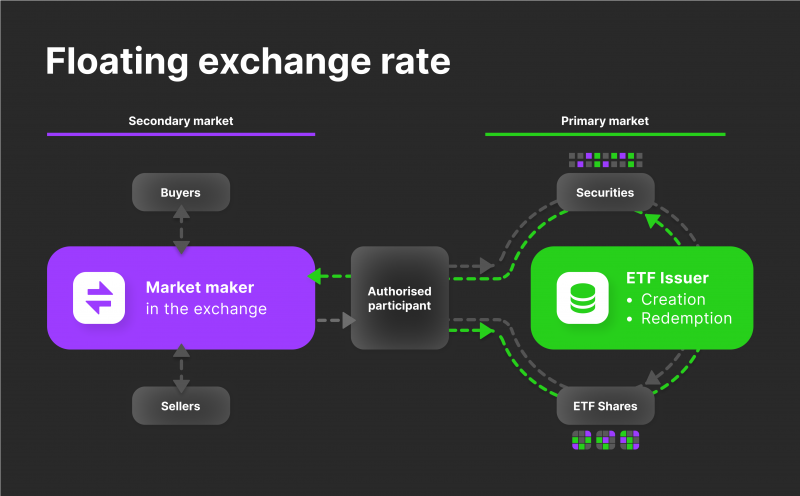
Creation and Structure:
Approved Participants (APs):
These are accredited organizations that are permitted to issue and redeem ETF shares, such as sizable investment banks or brokerages.
APs usually maintain accounts with custodians that safeguard the underlying assets as well as the ETF issuer. They are essential to preserving the price monitoring and liquidity of the ETF.
Underlying assets :
Spot Bitcoin ETFs: These hold actual Bitcoin as the primary asset.
Bitcoin is purchased by the APs on cryptocurrency exchanges or OTC markets.
Custodians, specialized firms with robust security measures, store the Bitcoin in cold wallets or hot wallets.
💡The assets currently in review for Bitcoin. But can be expected to extend to assets like ETH and Ripple
Bitcoin Futures ETFs: These hold Bitcoin futures contracts, not actual Bitcoin.
APs buy and sell these contracts on regulated futures exchanges
The ETF's performance is primarily driven by the price movements of these futures contracts.
Trading on the Exchange:
Secondary Market Trading:
Once the creation units are obtained by authorized participants, they can be traded on the secondary market, such as a stock exchange.
Individual investors buy and sell these ETF shares through brokerage accounts at market prices.
Market Price vs. Net Asset Value (NAV):
The market price of an ETF share may fluctuate throughout the trading day based on supply and demand.
The Net Asset Value (NAV) represents the per-share value of the ETF's underlying asset(Bitcoin). While the NAV is calculated at the end of each trading day.
Having understood the structure of an ETF. We will understand that most of the assets and the movement of shares for them are handled offchain.
This introduces a need for trust towards the financial organizations handling them.
And these organizations trade these assets on a OTC or exchange that they trust in.
Hence, users often opt for the more reputable institutions to handle their funds.
This trust can be even strengthened by introducing transparency to the management of shares and underlying assets and utilizing smartcontracts to handle the funds instead of wallets.
- This also introduces a level of automation where the financial institutions have only power over how your funds move across the exchanges but cannot have tangible ownership over them.
These give rise to the question , can hybrid ETFs be built and if so how would they look.
Decentralized hybrid onchain ETF models
In the current world decentralized Blockchain applications, The business logic and funds are handled onchain using immutable programs called Smart Contracts.
Different functionalities can be implemented in smart contracts ranging from deposits of assets to integration of exchanges.
However we will soon understand that such programmability is only possible in the chains that were later introduced like Ethereum and Ripple. Which is inherently absent in Bitcoin infrastructure. This issue has been solved by the Introduction of wrapped tokens which exist on other chains and are backed 1 : 1 by native bitcoin.
Many chains like Arbitrum , Ethereum and stacks have introduced Wrapped BTC(WBTC) and are regularly traded on DEXes.
One such infrastructure striving to achieve a seamless integration of EVM's programmability with Bitcoin's security is Interlay's BOB (Build on Bitcoin).BOB is the first Bitcoin L2 with full EVM compatibility. Best of both worlds.

While interlay works towards seamless integration of substrate Chains with Bitcoin, BOB explores the EVM Infrastructure.
Interlay issues iBTC and kBTC based on the network. It accepts KSM or BTC as collateral and mints kBTC.
We will explore the interlay ecosystem in upcoming guides.
On-chain Hybrid ETF architecture on BOB
We will now venture into discussing how we can design a reliable Hybrid ETF model. Even though what we discuss here cannot be fully translated to a flawless infrastructure , It definitely will lay groundwork to how it can be built.

Smart Contract structure :
Creation and Redemption Logic: Includes functions to handle the creation and redemption processes. Authorized participants interact with the smart contract to exchange assets for ETF shares (creation) or ETF shares for assets (redemption). These shares can follow the standard of fungible tokens on EVM.
Decentralized Exchange Integration:
Interfaces with decentralized exchanges or liquidity pools to list and trade ETF tokens. This ensures liquidity and allows users to buy or sell shares at market prices.
Oracle Integration:
Price Feed: Contracts will be integrated with Acurast's decentralized oracles deployed on BOB to obtain real-time data, such as asset prices . This ensures accurate pricing information for the ETF's underlying assets.
Fee Structure Module:
Fee Calculation: We saw that the proposals presented recently charged various percentages of Fee for managing ETFs. This module defines the fee structure, automatically deducting management fees or other costs. Fees might be collected in the form of underlying assets or ETF tokens.
Trading interface and Easy onboarding:
This is an important aspect of the platform and needs perfect execution. Since the Target audience is Investors who do not fully associate with the Blockchain technology and cannot fully understand the nuances of Blockchain. Concept abstraction is very much necessary.
To preserve self custodian narrative and ownership, We can implement the Account Abstraction and gasless transactions to make asset translation a simple process. BOB supports meta-transactions using the OpenGSN and ERC-2771 standard enabling smooth UX.
Offchain Components
Compliance Module: Incorporates features to ensure regulatory compliance with relevant financial regulations and reporting requirements. This includes the KYC and AML checks needed for compliance with the regional Governing body.
Tax Reporting Modules : tax laws of given region can be automated and deducted accordingly from within the platform
Order and Liquidity Management systems : These keep track and enable the order completion and maintain stable liquidity for underlying asset.
Monitoring Tools: Implements tools for monitoring the health and performance of the smart contract and associated modules.
Analytics: Provides analytics on trading volumes, asset composition, and other relevant metrics.
Audit Trails: Implements features for maintaining an audit trail of transactions and operations for transparency and compliance.
Disaster Management systems : Along with secure and compliant Program a Monitoring and Mitigation system is necessary since Blockchain Apps attract Bad Actors.
What we have listed are core components of a hybrid ETF model that can be adopted and scaled by Financial organizations. With the rise in Private blockchains and Rollups, Organizations can utilize such technologies for a Application specific blockchain model for themselves.
The infrastructural requirement of this model is comparable to current world ETF implementations and introduce Transparency Compliance and Security. Some of the main motives behind the Blockchain and crypto revolution.
Advantages of Decentralized ETF model
Enhanced Security: The decentralized nature of the blockchain ensures transparency, immutability, and resistance to tampering, reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access.
Elimination of Single Points of Failure: reduces vulnerabilities associated with centralized entities, making the ETF less susceptible to hacking, downtime, or manipulation.
Direct Ownership and Control: This model aligns with the principles of cryptocurrency, where individuals control their holdings and have the sovereignty to manage their holdings.
Global Accessibility and Compliance : The Programmability of the smartContracts and the system to accommodate the various rules and regulations of local authorities across the globe allows everyone to access these investments opportunities.
Reduced Counterparty Risk: No matter how reputable a financial organization is there is a risk of mismanagement and therefore loss of funds. Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate certain processes, reducing such events.
Intraday Trading 24/7: Investors have greater flexibility to respond to market changes and execute trades whenever they want. Since a DEX is always operational. And the organization can still keep track of all asset transfers by querying the blockchain.
Transparent Rulesets and reduced third party interference: Decentralized systems are resistant to censorship , ensuring the ETF's seamless operation.
Conclusion
While the vision of a decentralized ETF presents a promising future, it's important to acknowledge that this proposed infrastructure lays the groundwork rather than providing a flawless solution. While regulatory roadblocks, scaling issues, and mass adoption hurdles persist, projects like Interlay's BOB show persistent efforts are made in advancement of blockchain technology while complying to the decentralization narrative.
One takeaway being , the hybrid onchain ETF model envisions a future where investment agents are not only secure and transparent but also accessible to a global audience while in harmony with the regional governing bodies. As the industry continues to innovate, the proposed model sets the stage for a more decentralized, efficient, and inclusive approach to investment models .
With the industry innovating, it's high time Bitcoin ETFs get the go-ahead. The world is ready.
Stay Flashy ✨.
