
Photo by DrawKit Illustrations on Unsplash
Scaling ETH: Evolution of L2s and what Dencun upgrade mean to them.
Introduction
Layer 2 blockchains are designed to scale Ethereum by introducing higher TPS (throughput), Lower fees and enhanced data availability. They do so by offloading computation from the main L1(Ethereum) and storing the states and state changes off-chain or within the L2.
In the latest upgrade Dencun, Ethereum introduces approaches which will enable these rollups to interact with the mainet in a much more cost efficient manner. This in return allows rollups to increase their performance and reduce cost for the users on top of them. Let us take a look at the new features introduced in this upgrade.
What's new
The latest upgrade brings important changes to the execution and consensus layers.
The changes made to the consensus layer is named Deneb and the changes made to the execution layer is called Cancun.
Proto-DankSharding
Image Credits: Moralis
The main feature introduced to this upgrade is proto-Danksharding which allows temporary storage of large data on Ethereum chain. This is leveraged by rollups to store transaction metadata on the L1 temporarily. They also introduced new commitment scheme for proving the validity of Commits. These blobs are capable of holding large data as compared to current approach that uses calldata. The cost is significantly low and less punishing to the network operators as the data stored is temporary. This upgrade is the initial steps of the Surge Phase which is focused on scaling ethereum through rollups. And the feature is currently experimental and expected to achieve sharding on a larger scale by the end of surge phase
New EIPs introduced
EIP-1153: Transient storage opcodes. These Opcodes are introduced to optimize data storage. They are deleted after execution of the transaction.
EIP-4788: Beacon block root in the EVM. It commits the latest block root of the beacon chain to a smart contract for transparency between execution and consensus layers.
EIP-4844: Shard Blob Transactions. Introduces more affordable Data availability for rollups. Also known as Proto-DankSharding.
EIP-5656: MCOPY - Memory copying instruction. It introduces a much more efficient way to copy memory.
EIP-6780: SELFDESTRUCT only in same transaction. Only transfers assets to target without deleting any data unless the opcode is called in the same transaction the contract is created in.
EIP-7044: Perpetually Valid Signed Voluntary Exits. Lock validator voluntary exit signature domain on Capella for perpetual validity. Currently, signed voluntary exits are only valid for two upgrades
EIP-7045: Increase Max Attestation Inclusion Slot. Increases the time in which an attestation can be included as part of a Beacon Chain block.
EIP-7514: Add Max Epoch Churn Limit. This proposal aims to mitigate the negative externalities of very high level of total ETH supply staked before a proper solution is implemented. In other words, this proposal accepts the complexities of changing the rewards curve and is meant only to slow down growth.
EIP-7516: BLOBBASEFEE opcode .The intended use case would be for contracts to get the value of the blob base-fee. This feature enables blob-data users to programmatically account for the blob gas price.
What it means for Rollups and users
For Rollups-
Drastically Reduced Fees: Dencun brings a significant advantage to rollups by slashing transaction fees. Storing transaction data on the mainnet used to be costly, but with Dencun's introduction of "blobs," a more economical temporary storage solution for rollup data, overall transaction processing costs are greatly diminished.
Heightened Competitiveness: Through Dencun, rollups can now offer transactions at a fraction of the cost compared to the mainnet. This not only enhances their competitiveness with traditional blockchains but also encourages broader adoption of rollup-based applications.
For Users-
Speedier and More Affordable Transactions: Users engaging with applications built on rollups will notice a substantial improvement. Transactions will be processed faster and at significantly lower costs, thanks to Dencun's impact on reducing rollup fees.
Expanded Participation: Lower transaction expenses have the potential to attract a wider user base to the Ethereum ecosystem. This could result in increased adoption of decentralized applications (dApps) and DeFi protocols built on rollups.
A Glimpse of Future Possibilities: Dencun paves the way for exciting prospects such as "gas-less" experiences. In forthcoming scenarios, applications might cover transaction fees on behalf of users, creating a smoother user experience with minimal friction.
Evolution of Rollups
As we can clearly understand that Ethereum vision of scalability largely emphasizes on Rollups. It is important to understand the advancements made in L2s to address the Ethereum's trilemma of security scalability and Decentralization, Let's take a look at some of the types.
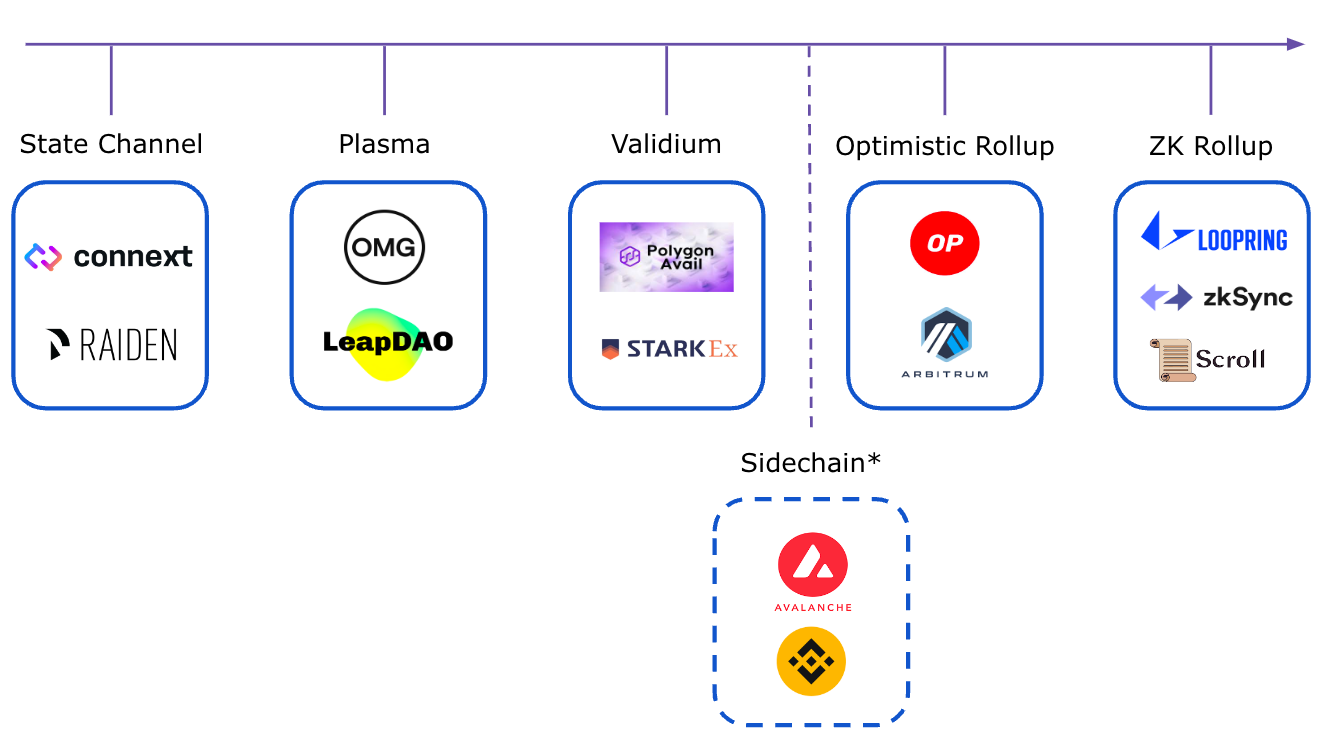
Image credits: AlphaVentures
Early Rollups:
The fundamental concept involves aggregating transactions off-chain, validating them using cryptographic evidence, and then submitting this evidence to the mainnet for final confirmation. This approach alleviates the burden on the main chain, resulting in quicker and more cost-effective transactions.
There are primarily two variants:
Optimistic Rollups: These presume the validity of transactions by default. Any individual can dispute a fraudulent transaction with a proof of fraud, although there is a waiting period for resolution.
ZK-Rollups: These employ zero-knowledge proofs to verify transaction validity cryptographically without disclosing the actual data. While this method facilitates faster verification, it necessitates more intricate cryptographic techniques.
Introducing Based Rollups: A Fresh Approach
Based Rollups present a novel method for transaction sequencing:
Capitalizing on Mainnet Security: Instead of maintaining their own sequencer, Based Rollups depend on the mainnet's security for transaction ordering. This approach yields several benefits such as:
Accelerated Finality: Transactions can achieve finality more swiftly compared to optimistic rollups, which often entail waiting periods.
Mitigated Decentralization Concerns: Some contend that centralized sequencers in conventional rollups pose security risks. Based Rollups mitigate this by utilizing the decentralized sequencer of the mainnet.
Enhancing Security with Based Contestable Rollups
Based Contestable Rollups enhance security by incorporating an additional layer of protection:
Validating Transaction Legitimacy: Similar to optimistic rollups, anyone can furnish proof if they suspect a transaction to be invalid. This serves as a safeguard within the system in case of errors by the mainnet sequencer.
Based Contestable Rollups (BCR) with Multiproofs
Based contestable rollups (BCRs) take the concept of based rollups a step further by incorporating multiproofs:
Challenging with Evidence: Similar to traditional optimistic rollups, anyone can submit a fraud proof if they believe a transaction is invalid. However, BCRs leverage multiproofs. These proofs can be:
Validity Proofs: Demonstrate a transaction is indeed valid within the rollup.
Invalidity Proofs: Prove a transaction is fraudulent.
Enhanced Security: Multiproofs allow validators to efficiently verify the validity of the entire rollup or identify specific invalid transactions. This adds an extra layer of security compared to basic based rollups.
Improved Efficiency: By using multiproofs, validators can potentially process challenges faster and with less data compared to traditional fraud proofs in optimistic rollups.
Even though such level of decentralization is not yet achieved, Protocols like Taiko, Nil Foundation, Arbitrum and Optimism strive to innovate in these crucial advancements. Some adopting ZK and some optimistic.
Conclusion
The Dencun update serves as a crucial stepping stone towards a more scalable and user-friendly Ethereum. By empowering rollups with significantly reduced transaction fees, it paves the way for faster, cheaper transactions and wider adoption of decentralized applications. This highlights the growing importance of rollup solutions (L2s) in Ethereum's scaling roadmap.
However, the quest for a truly secure and decentralized future continues. As Ethereum evolves, we can expect further innovations in rollup technology that address these crucial aspects. The Dencun update marks an exciting chapter, but it's only the beginning of the innovations for a more secure Ethereum ecosystem.
Stay Flashy✨
